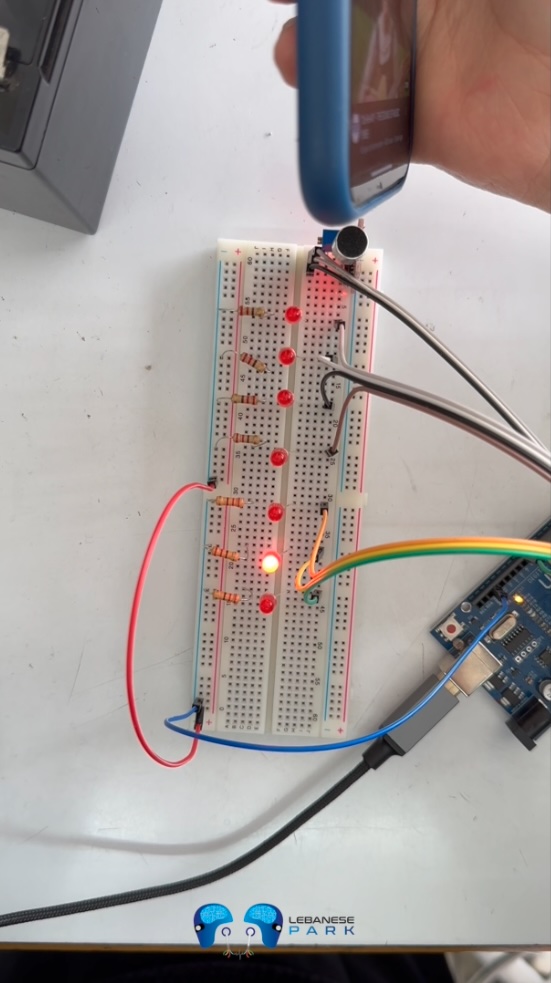
Below is the short video published on YouTube:
Here’s the code:
// ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Project: Singing bowls illumination
// Description: It turns on a different colour depending on which Chakra is played
// Engineer: Alberto Lopez
// More: https://misCircuitos.com
// Date: 16 – nov – 2022 Chiang Mai (Thailand)
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
define DEBUG_MODE //Comment when finish debuging
//—————————————————————————//
int in[128];
byte NoteV[13]={8,23,40,57,76,96,116,138,162,187,213,241,255}; //data for note detection based on frequency
//byte NoteV[13]={8,23,40,57,76,96,116,138,162,187,213,241,255}; //data for note detection based on frequency 440Hz tuning
float f_peaks[5]; // top 5 frequencies peaks in descending order
// pins
const int Mic_pin = A0; // change as per Microphone pin
const int red_pin = 2; //C
const int orange_pin = 3;
const int yellow_pin =4; //E
const int green_pin = 5;
const int blue_pin = 6; //G
const int blueDark_pin = 7;
const int purple_pin = 8; //B
int MINIMUM_SOUND = 383; //minimim sound level threshold to start lighting
//variables
int note;
//—————————————————————————//
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(“Singing Bowls correctly initialized”);
Serial.println(“v1.0 17-nov-2022 Alberto Lopez: misCircuitos.com \n”);
//Declare the LED pins as output
pinMode(red_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(orange_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(yellow_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(green_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(blue_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(blueDark_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(purple_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(A0, INPUT);
MINIMUM_SOUND=0;
for(int i=0;i<20;i++)
{
MINIMUM_SOUND+=analogRead(A0);
}
MINIMUM_SOUND=MINIMUM_SOUND/20;
Serial.println(MINIMUM_SOUND);
//testLED(); //Debug LED and light all
}
void loop()
{
//delay(10); //slow down the loop
//testLED();
//debug mic
//int lecturaMic = analogRead(Mic_pin);
//Serial.print(“volumen:”); Serial.println(lecturaMic);
note = ReadNote();
resetLED();
switch(note)
{
case 0: //RED
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number C”);
digitalWrite(red_pin,HIGH);
break;
case 2: //ORANGE
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number D”);
digitalWrite(orange_pin,HIGH);
break;
case 4: //YELLOW
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number E”);
digitalWrite(yellow_pin,HIGH);
break;
case 5: //GREEN
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number F”);
digitalWrite(green_pin,HIGH);
break;
case 7: //LIGHT BLUE
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number G”);
digitalWrite(blue_pin,HIGH);
break;
case 9: //DARK BLUE
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number A”);
digitalWrite(blueDark_pin,HIGH);
break;
case 11: //PURPLE
//Serial.println(“The Bowl number B”);
digitalWrite(purple_pin,HIGH);
break;
default:
resetLED();
}
ifdef DEBUG_MODE
switch(note)
{
case 0:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number C”);
break;
case 2:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number D”);
break;
case 4:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number E”);
break;
case 5:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number F”);
break;
case 7:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number G”);
break;
case 9:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number A”);
break;
case 11:
Serial.println(“The Bowl number B”);
break;
}
endif
}//close loop
void resetLED()
{
digitalWrite(red_pin,LOW);
digitalWrite(orange_pin,LOW);
digitalWrite(yellow_pin,LOW);
digitalWrite(green_pin,LOW);
digitalWrite(blue_pin,LOW);
digitalWrite(blueDark_pin,LOW);
digitalWrite(purple_pin,LOW);
}
void testLED(){
Serial.println(“LED test debug mode”);
int speed = 2000;
while(1){
resetLED();
digitalWrite(red_pin,HIGH);
Serial.println(“RED”);
delay(speed);
digitalWrite(orange_pin,HIGH);
Serial.println(“ORANGE”);
delay(speed);
digitalWrite(yellow_pin,HIGH);
Serial.println(“YELLOW”);
delay(speed);
digitalWrite(green_pin,HIGH);
Serial.println(“GREEN”);
delay(speed);
digitalWrite(blue_pin,HIGH);
Serial.println(“BLUE”);
delay(speed);
digitalWrite(blueDark_pin,HIGH);
Serial.println(“BLUEDARK”);
delay(speed);
digitalWrite(purple_pin,HIGH);
delay(speed);
}
}
//—————————–Tone Detection Function———————————————-//
// This code won’t work for any board having RAM less than 2kb,
int ReadNote()
{ long unsigned int a1,b,a2;
float a;
float sum1=0,sum2=0;
float sampling;
a1=micros();
for(int i=0;i<128;i++) //DATA ACQUISITION
{
a=analogRead(Mic_pin)-MINIMUM_SOUND; //rough zero shift
//utilising time between two sample for windowing & amplitude calculation
sum1=sum1+a; //to average value
sum2=sum2+aa; // to RMS value a=a(sin(i3.14/128)sin(i3.14/128)); // Hann window in[i]=10a; // scaling for float to int conversion
delayMicroseconds(195); // based on operation frequency range
}
b=micros();
sum1=sum1/128; // Average amplitude
sum2=sqrt(sum2/128); // RMS
sampling= 128000000/(b-a1); // real time sampling frequency
//for very low or no amplitude, this code wont start
//it takes very small aplitude of sound to initiate for value sum2-sum1>3,
//change sum2-sum1 threshold based on requirement
if(sum2-sum1>3){ //THRESHOLD TO START
FFT(128,sampling);
//EasyFFT based optimised FFT code,
//this code updates f_peaks array with 5 most dominent frequency in descending order
for(int i=0;i<12;i++){in[i]=0;} // utilising in[] array for further calculation
int j=0,k=0; //below loop will convert frequency value to note
for(int i=0; i<5;i++) { if(f_peaks[i]>1040){f_peaks[i]=0;}
if(f_peaks[i]>=65.4 && f_peaks[i]<=130.8) {f_peaks[i]=255((f_peaks[i]/65.4)-1);} if(f_peaks[i]>=130.8 && f_peaks[i]<=261.6) {f_peaks[i]=255((f_peaks[i]/130.8)-1);} if(f_peaks[i]>=261.6 && f_peaks[i]<=523.25){f_peaks[i]=255((f_peaks[i]/261.6)-1);} if(f_peaks[i]>=523.25 && f_peaks[i]<=1046) {f_peaks[i]=255((f_peaks[i]/523.25)-1);} if(f_peaks[i]>=1046 && f_peaks[i]<=2093) {f_peaks[i]=255*((f_peaks[i]/1046)-1);} if(f_peaks[i]>255){f_peaks[i]=254;}
j=1;k=0;
while(j==1)
{
if(f_peaks[i]<NoteV[k]){f_peaks[i]=k;j=0;}
k++; // a note with max peaks (harmonic) with aplitude priority is selected
if(k>15){j=0;}
}
if(f_peaks[i]==12){f_peaks[i]=0;}
k=f_peaks[i];
in[k]=in[k]+(5-i);
}k=0;j=0;
for(int i=0;i<12;i++)
{
if(k<in[i]){k=in[i];j=i;} //Max value detection
}
// Note print
// if you need to use note value for some application, use of note number recomendded
// where, 0=c;1=c#,2=D;3=D#;.. 11=B;
//a2=micros(); // time check
k=j;
/*
Serial.print(“note:”);
Serial.print(k);
Serial.println(“,”);
/ /
if(k==0) {Serial.println(‘C’);}
if(k==1) {Serial.print(‘C’);Serial.println(‘#’);}
if(k==2) {Serial.println(‘D’);}
if(k==3) {Serial.print(‘D’);Serial.println(‘#’);}
if(k==4) {Serial.println(‘E’);}
if(k==5) {Serial.println(‘F’);}
if(k==6) {Serial.print(‘F’);Serial.println(‘#’);}
if(k==7) {Serial.println(‘G’);}
if(k==8) {Serial.print(‘G’);Serial.println(‘#’);}
if(k==9) {Serial.println(‘A’);}
if(k==10){Serial.print(‘A’);Serial.println(‘#’);}
if(k==11){Serial.println(‘B’);}
*/
return k;
}
}
//—————————–FFT Function———————————————-//
// EasyFFT code optimised for 128 sample size to reduce mamory consumtion
float FFT(byte N,float Frequency)
{
byte data[8]={1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128};
int a,c1,f,o,x;
a=N;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++) //calculating the levels
{ if(data[i]<=a){o=i;} }
o=7;byte in_ps[data[o]]={}; //input for sequencing
float out_r[data[o]]={}; //real part of transform
float out_im[data[o]]={}; //imaginory part of transform
x=0;
for(int b=0;b<o;b++) // bit reversal
{
c1=data[b];
f=data[o]/(c1+c1);
for(int j=0;j<c1;j++)
{
x=x+1;
in_ps[x]=in_ps[j]+f;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<data[o];i++) // update input array as per bit reverse order
{
if(in_ps[i]<a)
{out_r[i]=in[in_ps[i]];}
if(in_ps[i]>a)
{out_r[i]=in[in_ps[i]-a];}
}int i10,i11,n1;
float e,c,s,tr,ti;
for(int i=0;i<o;i++) //fft
{
i10=data[i]; // overall values of sine cosine
i11=data[o]/data[i+1]; // loop with similar sine cosine
e=6.283/data[i+1];
e=0-e;
n1=0;
for(int j=0;j<i10;j++)
{
c=cos(e*j);
s=sin(e*j);
n1=j;
for(int k=0;k<i11;k++)
{
tr=c*out_r[i10+n1]-s*out_im[i10+n1];
ti=s*out_r[i10+n1]+c*out_im[i10+n1];
out_r[n1+i10]=out_r[n1]-tr;
out_r[n1]=out_r[n1]+tr;
out_im[n1+i10]=out_im[n1]-ti;
out_im[n1]=out_im[n1]+ti;
n1=n1+i10+i10;
}
}
}//—> here onward out_r contains amplitude and our_in conntains frequency (Hz)
for(int i=0;i<data[o-1];i++) // getting amplitude from compex number
{
out_r[i]=sqrt((out_r[i]out_r[i])+(out_im[i]out_im[i])); // to increase the speed delete sqrt
out_im[i]=(iFrequency)/data[o]; /
Serial.print(out_im[i],2); Serial.print(“Hz”);
Serial.print(“\t”); // uncomment to print freuency bin
Serial.println(out_r[i]);
*/
}
x=0; // peak detection
for(int i=1;iout_r[i-1] && out_r[i]>out_r[i+1])
{in_ps[x]=i; //in_ps array used for storage of peak number
x=x+1;}
}
s=0;
c=0;
for(int i=0;i<x;i++) // re arraange as per magnitude
{
for(int j=c;j<x;j++)
{
if(out_r[in_ps[i]]<out_r[in_ps[j]])
{s=in_ps[i];
in_ps[i]=in_ps[j];
in_ps[j]=s;}
}
c=c+1;
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) // updating f_peak array (global variable)with descending order
{
f_peaks[i]=(out_im[in_ps[i]-1]*out_r[in_ps[i]-1]+out_im[in_ps[i]]*out_r[in_ps[i]]+out_im[in_ps[i]+1]*out_r[in_ps[i]+1])
/(out_r[in_ps[i]-1]+out_r[in_ps[i]]+out_r[in_ps[i]+1]);
}}
//————————————————————————————//